Push Protocol, the leading web3 communication layer, has proposed a major upgrade with the introduction of Pre-PIP (Push Improvement Proposal) for Cross-Chain Requests (CCR). This proposal aims to enable users to interact with Push Protocol smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain from any blockchain network, whether it’s EVM-based or non-EVM. Once CCR is implemented, users will be able to stay on their preferred blockchain while accessing Push Protocol's services, offering enhanced convenience and flexibility.
What is CCR (Cross-Chain Requests) and its impact?
In the current Push Protocol architecture, performing any important task related to channels like creating a channel, modification of a channel, changing a channel’s state, etc, requires the user/protocol to interact with the Push Smart Contract which is only deployed on Ethereum Blockchain.
This led to a bad user experience for the user/protocol as they need to switch to the Ethereum network for any interaction they might want to do with the Push Core contract. This is currently a friction point for users who primarily operate on other EVM-compatible chains and even non-EVM users.
Cross-chain requests will eliminate the need to switch to the Ethereum Network making it possible to create a channel, use Push services, or interact with Push Protocol’s Ethereum smart contract from any blockchain they like, whether it’s another EVM chain or non-EVM chain.
Additionally, this was not just something that users faced but more for Push Protocol as it limits Push Protocol's ability to tap into other chains and help solve the communication/notification issues of those chains adequately. This constraint hinders the protocol from reaching a broader audience and solving communication issues across diverse blockchain environments.
Therefore, by enabling the Cross-Chain Request feature, Push Protocol can primarily significantly enhance the UX for average users as well as channel creators/managers from not just Ethereum but multiple other EVM/Non-EVM chains as well. It also allows the protocol to expand its market reach, attract users from different chains, and foster a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem.
Importance of CCR (Cross-Chain Requests):
The Cross Chain Requests (CCR) feature is crucial for the future success and growth of the Push Protocol:
- Enhanced User Experience: The CCR feature will significantly enhance user experience by eliminating the need for users to switch networks or manually bridge tokens to interact with the Push Core contract on Ethereum. This streamlined process will allow users to perform key actions like channel creation and incentivize chat requests directly from their preferred blockchain, reducing both complexity and transaction costs. By making these features accessible from various chains, CCR removes barriers for new and existing users, fostering a more inclusive and user-friendly environment.
- Broader Reach: The CCR feature will expand the reach of Push Protocol across the blockchain ecosystem. By enabling interactions from multiple EVM and non-EVM chains, CCR will not only broaden the protocol's user base but also tap into diverse blockchain communities that might benefit from Push’s communication and notification features. This increased accessibility helps Push Protocol grow its market presence and integrate with a wider range of blockchain projects, ultimately supporting the development of a more interconnected and collaborative blockchain network.
- Revolutionizing Web3 Communications: CCR future-proofs Push Protocol against the rapid evolution of the blockchain space. As new chains and technologies emerge, CCR’s cross-chain capabilities ensure that Push Protocol remains adaptable and relevant. By leveraging established technologies like Wormhole’s NTT framework and Relayers, CCR positions Push Protocol to embrace future advancements and continue delivering value to its users across an ever-expanding blockchain landscape.
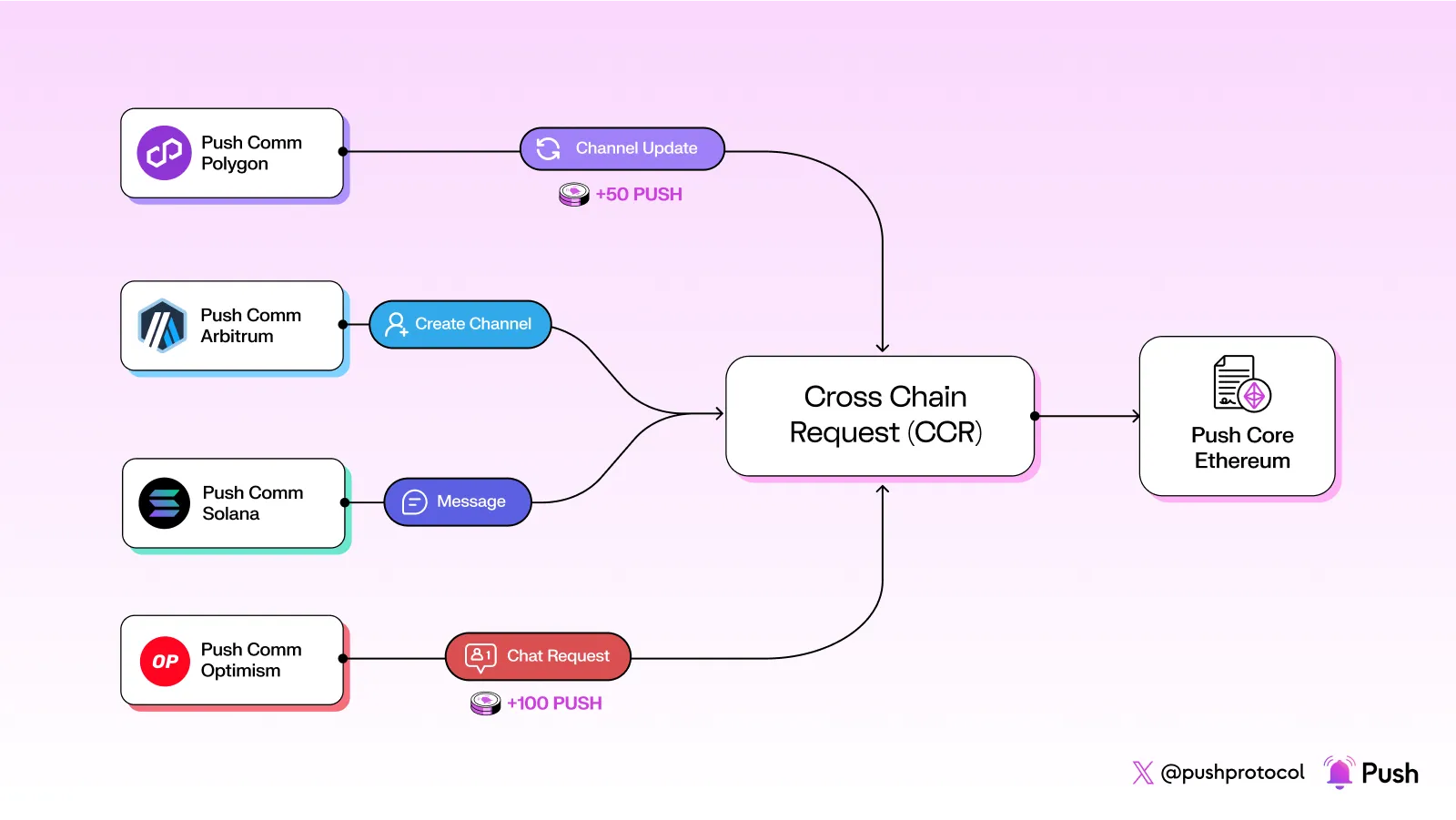
Here’s a simple overview of how CCR works:
- Initiate Request: A user on another blockchain (like Polygon) wants to perform an action, such as creating a new channel for sending notifications.
- Submit Details: The user uses a special function on the Push Communicator contract on their preferred blockchain to submit the request, providing the necessary details and approving the $PUSH tokens for the action.
- Send Data and Tokens: The Push Communicator contract validates the input, creates a message payload, and uses Wormhole Relayers to securely send this payload and the $PUSH tokens to the Push Core contract on Ethereum.
- Process Request: On Ethereum, the Push Core contract receives the message and tokens, decodes the request, validates it, and performs the required action.
- Completion: The request is completed on Ethereum, and any unused native tokens are refunded to the user on their original blockchain.
Visualizing Channel Creation with the CCR feature
Imagine Bob, a Polygon user, wants to create a channel for sending notifications.
Previously, he'd need to switch to Ethereum, bridge tokens, and change networks. With CCR, Bob simply uses the familiar Push Communicator contract on Polygon.
The contract acts as a bridge, relaying Bob's request (channel details) and the required PUSH tokens (bridged via Wormhole) to the Push Core contract on Ethereum.
All behind the scenes, without Bob ever leaving Polygon! This creates a seamless experience for users on any chain, opening Push Protocol to a wider audience.
Why Not Just Deploy Push Core Everywhere?
While putting Push Core on every blockchain might seem easy, it's quite tricky.
It would be hard to manage separate fees and keep all the information on different chains in sync, which could even be risky.
That's why we're improving the existing Push Communicator contracts to handle these requests. We'll also use a reliable system called Wormhole to securely send information and tokens between blockchains. This way, everything works smoothly without needing Push Core on every chain. For more details check out here.
Implementation: How we will build CCR:
To implement Cross-Chain Requests (CCR), we will:
- Enable $Push Token for multi-chain support.
- Build cross-chain support in the Push Communicator and Push Core Contract.
- Use Wormhole’s Relayer Interface and NTT framework for token transfers across chains.
- Equip the Push Communicator to handle cross-chain actions like channel creation and requests.
- Modify the Push Core Contract to process cross-chain payloads.
- Conduct security audits and deploy the updated contracts on the testnet and mainnet.
For more details on the implementation of CCR check out here.
The Future of Push Protocol:
CCR feature is a significant step forward for Push Protocol. It paves the way for a more interconnected and user-friendly communication layer within the ever-expanding blockchain landscape.
Stay tuned for further updates as we implement CCR and empower users to unlock the full potential of Web3 communication!