- Overview
- What is Push Chain?
- How does Push Chain work?
- Why is Push Chain unique for users?
- What Makes Push Chain Innovative?
- What problems does Push Chain solve?
- What apps can you build on Push Chain?
- Technical
- Why L1 and not an L2?
- Is Push Chain EVM Compatible?
- Will Push Chain be compatible with both EVM and non-EVM chains?
- Why create a new blockchain when existing ones like Ethereum and Solana already exist?
- What does shared state blockchain mean?
- How does Push Chain achieve shared state?
- What consensus mechanism does Push Chain use?
- How do transaction fees work on Push Chain?
- What does True Universal Chain mean?
- Competitors
- What sets Push Chain apart from other Universal Solutions?
- How is this different from bridges or messaging layers?
- How is Push Chain different from LayerZero?
- How is Push Chain different from Wormhole?
- How is Push Chain different from Axelar?
- How is Push Chain different from Chainlink CCIP?
- How is Push Chain different from Particle Network?
- How is Push Chain different from AggLayer?
- How is Push Chain different from Cosmos?
- How is Push Chain different from Polkadot?
- Token Related
- Will there be a new token associated with Push Chain?
- Developers, Users and Node Operators
- Are there incentives for early adopters or node operators on Push Chain?
- What benefits does Push Chain offer to developers and users?
- How can developers start building on Push Chain?
- DAO and Grants
- How will the current governance system change when the new token launches?
- Doubts
- What Happens to Push Notification and Push Chat?
- Is this project a distraction from improving current services?
- Is Push Chain a shift away from Push Protocol's core focus on notifications and chat?
- How will the launch of Push Chain affect existing partnerships and integrations?
- How will Push Chain maintain decentralization while scaling?
- Are there any risks of centralization with Push Chain?
- Support and Engagement
- I need help, where can I contact Push Chain?
- Great, how can I contribute?
Overview
The place to find answers to all the popular questions the community has asked about Push Chain. Crowdsourced from Push Fam 🫶 and curated by the Push team 💪.
What is Push Chain?
Push Chain is a shared-state Layer 1 blockchain built to eliminate fragmentation across all chains.
By enabling seamless transactions from any chain (Ethereum, Solana, EVM or non-EVM), it lets any user interact with web3 apps without juggling multiple wallets, tokens or gas mechanics.
In short, Push Chain unites L1s 🤝 L2s 🤝 L3s under one cohesive layer.
How does Push Chain work?
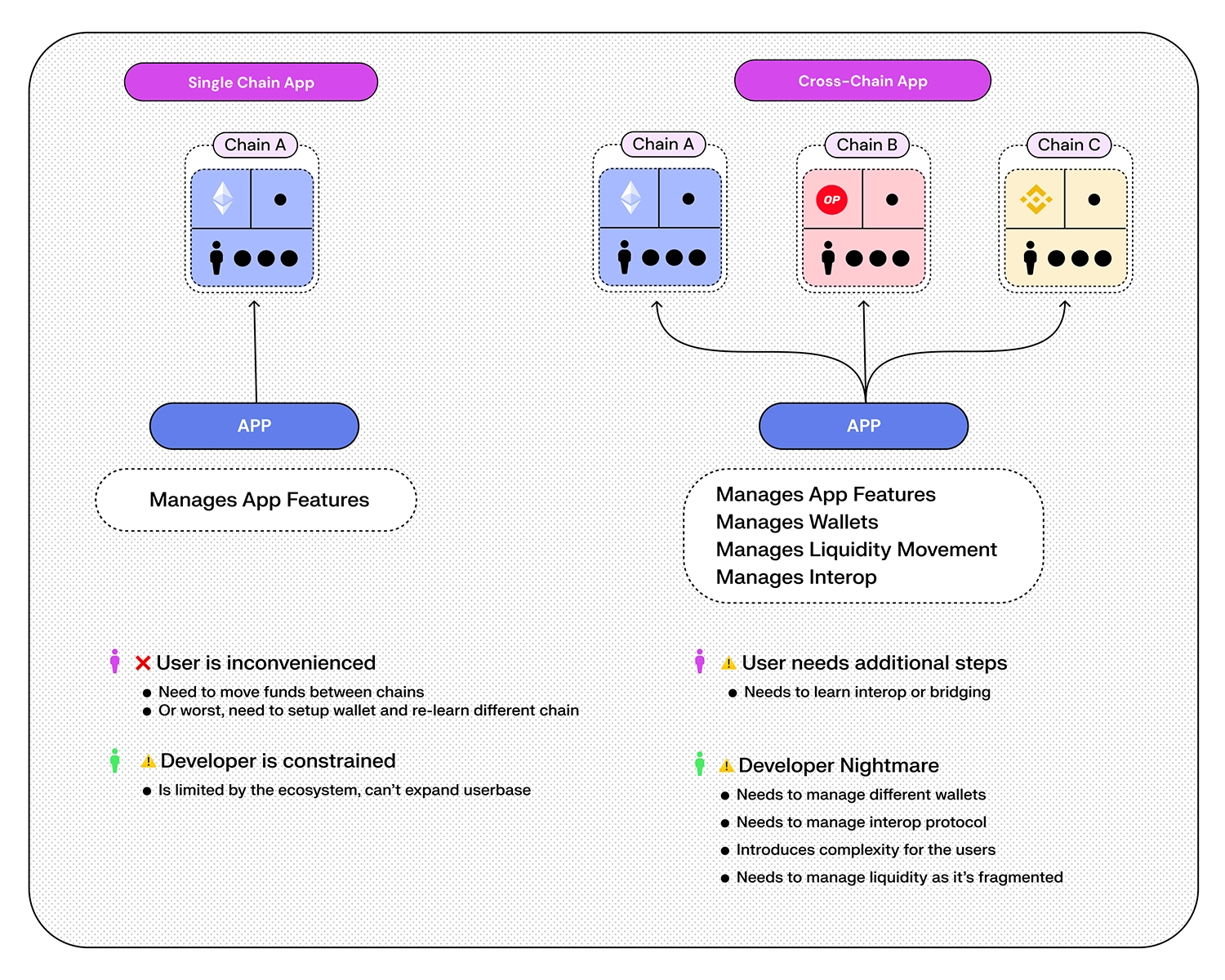
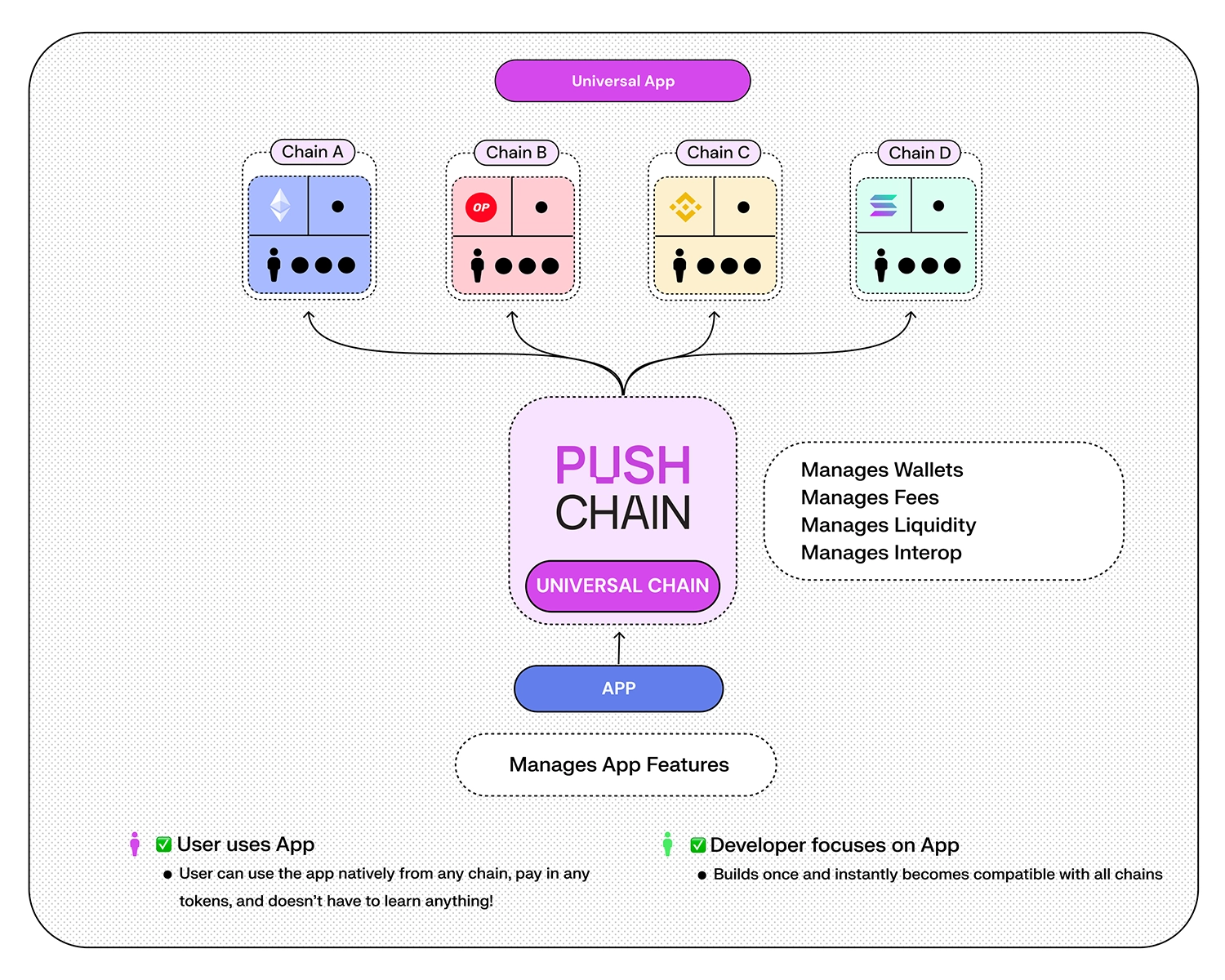
Push Chain takes a unique approach to solving the problem of fragmentation across all chains. Instead of relying on interoperability protocols, which add complexity for both users and developers, it takes a novel approach by building a true universal blockchain that can be natively used by any user from any chain.
To achieve this, Push Chain leverages several precompiles which are custom modules created to:
-
Recognize users of other chains - Universal address standard that extends the address of a user to be blockchain agnostic (based on CAIP-10 standards).
-
Map users to Push Chain - a Universal Executor Account (UEA) is deployed for each external-chain user. This module is used to deploy a smart account that then uses other precompiles to process the transactions.
-
Execute universal transactions - This is done by using USV (Universal Signature Verification) and UTXV (Universal Transaction Verifier) precompiles to verify and execute signatures and transactions from other chains.
-
Abstract away the complexities of the chain they are on - This is done by having universal gateway contracts on each chain that locks gas funds in native token of the chain (or any other compliant token) and then uses the UTXV precompiles to attribute the gas to UEA (Executor Account) and USV to execute the transaction.
This is an extremely powerful approach that allows users to interact with any app on Push Chain without worrying about the chain they are on or what wallet they are using as everything is abstracted away, for both the users and the developers.
Why is Push Chain unique for users?
Push Chain addresses specific gaps in the existing blockchains, such as interoperability, state access across chains, programmable solvers and wallet abstraction resulting in true full-stack interoperability. While existing blockchains are robust, they operate in their own eco-system and an aggregator to unite these chains are needed.
Push Chain's focus is on being a shared state chain for universal (interoperable) applications acting as a unifying layer where all chains can come together and use Push Chain as universal hub or do settlement between them.
It offers a new paradigm of web3 that works from Any Chain. For Any Wallet / User. And is suitable for Any App.
What Makes Push Chain Innovative?
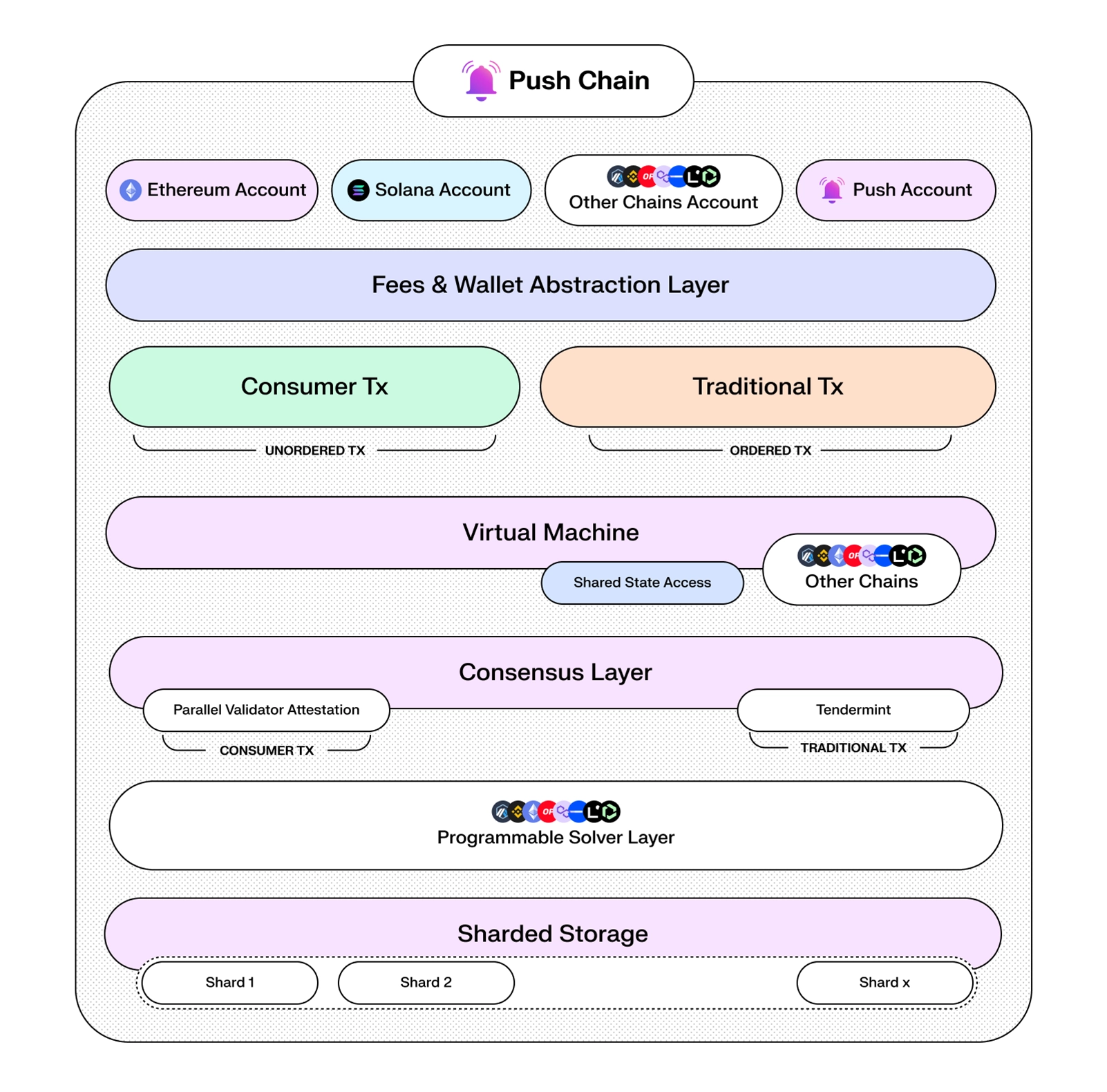
Push Chain is a Proof-of-Stake Layer 1 designed to eliminate fragmentation across every blockchain. Under the hood, it combines several key innovations:
-
Universal Smart Contracts
100% EVM compatible smart contracts that can be deployed with zero on-chain code changes. Once deployed, they become instantly compatible with users of all chains. -
True Universal Chain
Natively supports all chains and enables users to interact with the same app. No centralized relayers, bridges, or other hacks needed. -
Universal Fee & Wallet Abstraction
Allows users to interact with the app from any chain without worrying about gas or wallet mechanics. -
Single transaction for any chain
Users only ever sign one transaction, no matter which chain they’re on. -
Universal EVM
Push Chain is smart enough to natively recognize users of other chains and correctly attributes and maps the transactions to them.
Together, these features let you build universal web3 apps. Instead of "Uniswap on Ethereum" or "Uniswap on Polygon," a user simply becomes user of Uniswap — period.
What problems does Push Chain solve?
-
Fragmentation
Unites EVM & non-EVM chains under one shared-state L1, so users never need to hop networks or wallets. -
Interoperability
Native support for transactions from any blockchain and on-chain shared state. -
Finality
Instant, irreversible native finality in ~1-2 seconds – no more waiting or reorgs. -
Onboarding & UX
Social/email login, gas-in-any-token & any-wallet support for zero-friction access across chains. -
Universal Apps
Build once, deploy everywhere — any web3 app works seamlessly for any user on any chain.
What apps can you build on Push Chain?
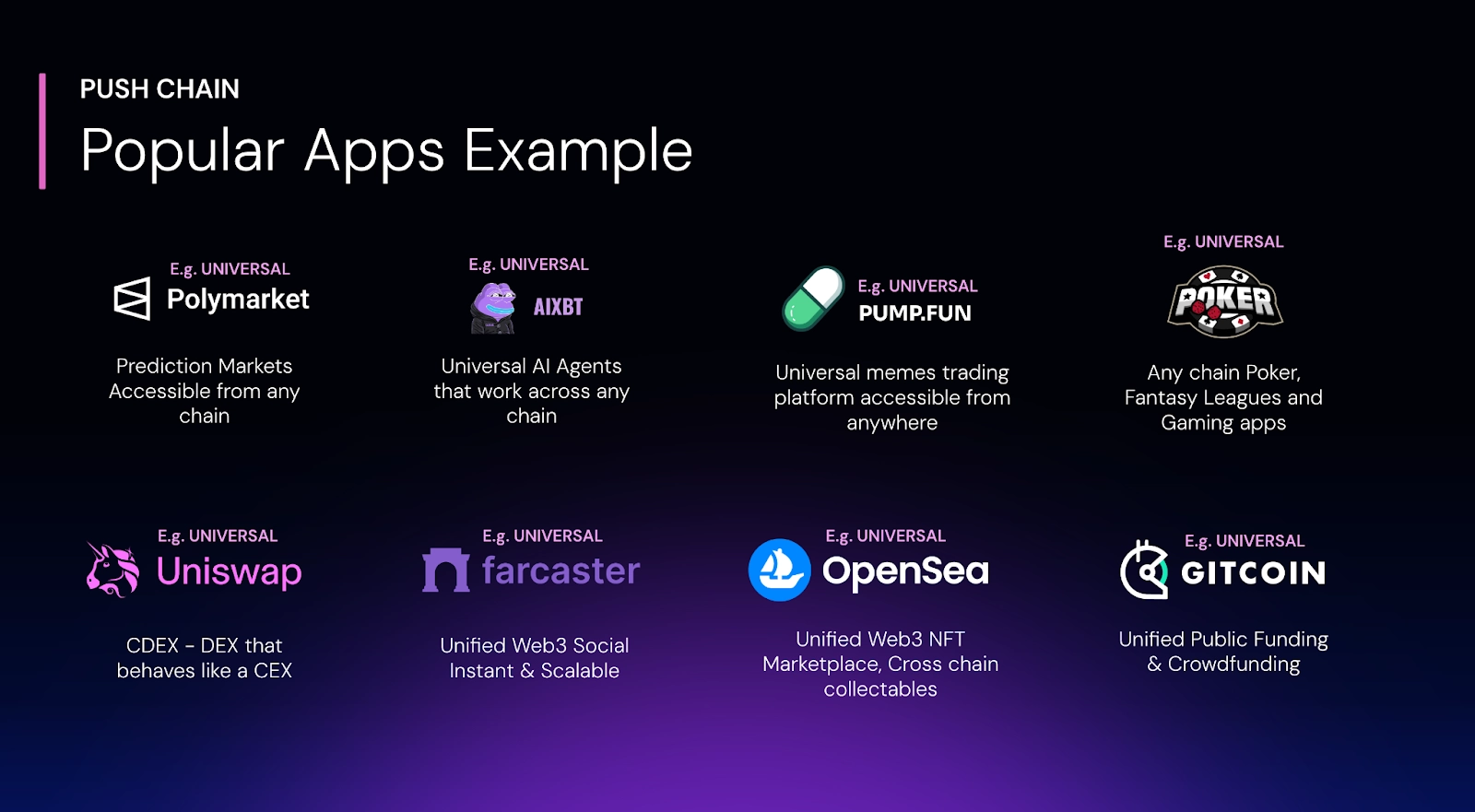
With Push Chain's shared-state, cross-chain architecture, the possibilities are endless. Here are just a few flagship examples:
-
Universal DEX
One swap UI for every liquidity pool–abstracted routing across all chains with the speed and UX of a CEX. -
Universal DeFi
A global bank in your browser: lending, borrowing, yield aggregators that span ecosystems without manual bridging. -
Universal AI Agents
Autonomous agents that pay and get paid in any token on any chain — perfect for subscription services, data bots, and more. -
Universal DAOs
Cross-chain governance where token holders vote and enact proposals irrespective of their origin chain. -
Universal Gaming
Multiplayer tournaments and in-game economies that unite players and assets from Ethereum, Solana, Polygon, and beyond. -
Universal Marketplace
Buy, sell, and trade NFTs and tokens from every chain in one consolidated marketplace. -
Universal Name Service
Human-readable names that resolve to wallets across multiple blockchains.
The apps and innovations that can happen on Push Chain are endless! Here are some more use cases to get you started. Builders can also check out the Documentation Hub to get started.
Technical
Why L1 and not an L2?
Push Chain is built to serve as a shared settlement layer and universal execution layer for all other blockchains—roles that only a standalone L1 can fulfill:
-
Native Cross-Chain Settlement
As an L1, Push Chain can directly finalize transactions from any chain without relying on external security models or fraud proofs. -
Universal Execution & State Access
Running its own consensus and state machine lets Push Chain interpret and execute transactions from Ethereum, Solana, and beyond — something an L2 — tied to one base layer — can’t do natively. -
No L2 Constraints or Delays
L2s inherit the latency, finality rules, and gas model of their host chain (plus bridging overhead). Push Chain avoids these bottlenecks by offering instant finality and universal fee abstraction at the base layer. -
True Shared State
To read & write the state of multiple chains within smart contracts, you need direct, protocol-level access—only available at the L1 layer.
In short, only a purpose-built L1 can unify every chain under one cohesive execution and settlement layer — without extra complexity or added trust assumptions.
Is Push Chain EVM Compatible?
Yes, Push Chain is EVM compatible and much more. It supports:
- EVM Smart Contracts: Deploy Solidity contracts just like on Ethereum
- Ethereum Tooling: Use MetaMask, Hardhat, Remix, and other familiar tools
- Universal Extensions: Additional precompiles for cross-chain functionality
- Multi-VM Support: (Roadmap) Support for other VMs like SVM (Solana), MoveVM, etc.
This means developers can:
- Port existing Ethereum dApps with minimal changes
- Use familiar development workflows and tools
- Access enhanced cross-chain capabilities through Push Chain's universal features
In practice, users and apps from any chain can interact with Push Chain apps seamlessly — no matter the underlying VM.
Will Push Chain be compatible with both EVM and non-EVM chains?
Yes! Push Chain is built to bridge every blockchain paradigm.
-
EVM Compatibility
Drop in your Solidity contracts and they run unchanged, leveraging Push Chain's EVM runtime. -
Non-EVM Support
Native precompiles (USV/UTXV) and the universal address standard let Push Chain validate and execute transactions from Solana, Bitcoin, Cosmos SDK chains, and more.
In practice, users and apps from any chain can interact with Push Chain apps seamlessly — no matter the underlying VM.
Why create a new blockchain when existing ones like Ethereum and Solana already exist?
Existing blockchains excel in their specific domains but create fragmentation:
- Ethereum: Great for DeFi but expensive and slow
- Solana: Fast and cheap but different tooling and ecosystem
- L2s: Solve scaling but create more fragmentation
Push Chain doesn't compete with these chains — it unifies them:
- Users can interact with Push Chain apps using their existing wallets (MetaMask, Phantom, etc.)
- Pay gas in their preferred tokens (ETH, SOL, USDC)
- Developers build once instead of deploying on multiple chains
- Liquidity and users from all chains can interact in the same apps
Push Chain is the missing piece that makes all existing chains work together seamlessly.
What does shared state blockchain mean?
Shared state refers to the present status of onchain data. A shared-state blockchain is one that has read-and-write access to its own state and the state of all other chains it interacts with.
A shared state chain is capable of handling data, liquidity, and users from any other chain.
How does Push Chain achieve shared state?
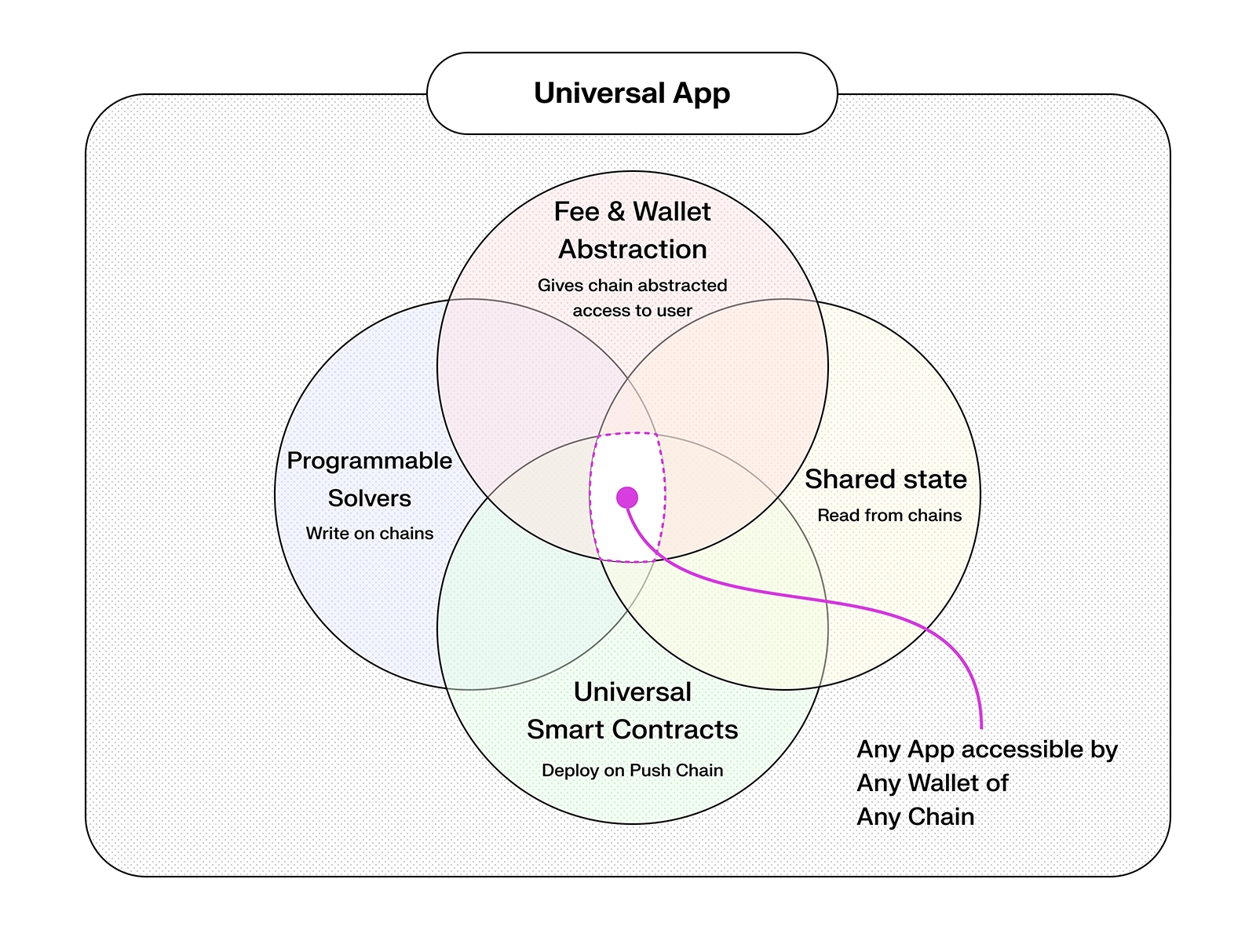
A traditional blockchain only knows its own ledger and wallet standard. Push Chain extends that model in four key ways:
-
Universal Wallet Compatibility
- Supports chain agnostic addresses from any chain (Ethereum, Solana, Bitcoin, Cosmos SDK, etc.)
- Signatures from any chain are verified via USV/UTXV precompiles, so users never switch wallets.
-
Universal Smart Contracts
- EVM contracts deploy unchanged but can natively verify and execute cross-chain transactions.
- Push Chain's runtime handles signature mapping and payload parsing for every supported network.
-
On-Chain Shared State
- Validators commit Merkle proofs of external chain state (via MPT roots) each block.
- Relayers fetch and submit leaf proofs on demand, so contracts can read any chain's data in real time.
-
Programmable Solvers
- A solver network executes atomic cross-chain workflows (e.g., swap on Chain A, mint on Chain B) under a single transaction.
- Developers write simple solver scripts; the network handles routing and execution.
Together, these features turn Push Chain into a shared-state L1 that enables universal apps to be native to all chains. A world where any user of any chain is able to access and interact with any app on any other chain.
Any Chain, Any App, Any User - One Push Chain
What consensus mechanism does Push Chain use?
Push Chain uses Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus, built on the CometBFT engine, with several enhancements:
- Fast Finality: Transactions are finalized in ~1–2 seconds, with deterministic finality (no reorgs)
- Energy Efficient: PoS is environmentally sustainable compared to PoW
- Validator Network: Decentralized network of validators securing the chain
- Slashing Protection: Economic incentives ensure validator honesty
CometBFT’s battle-tested BFT consensus is optimized here for the unique requirements of universal transaction processing and cross-chain state management.
How do transaction fees work on Push Chain?
Push Chain revolutionizes fee payment with Universal Fee Abstraction:
- Pay in Any Token: Users can pay gas in ETH, SOL, USDC, or any supported token
- Cross-Chain Fee Payment: Pay fees from your origin chain without bridging
- Gasless Transactions: Apps can sponsor user transactions for seamless UX
- Dynamic Fee Market: Fees adjust based on network demand
This means users never need to acquire native Push Chain tokens just to interact with apps.
What does True Universal Chain mean?
A true universal chain is a blockchain that treats every other network as first class citizens—no bridges, no centralized relayers, and no compatibility hacks. It delivers:
-
Native Multichain Identity
Wallets from Ethereum, Solana, any EVM or non-EVM chains all sign, verify and execute natively on Push Chain. So users never switch accounts or are troubled by the complexities of multiple wallets. -
Unified Settlement
Transactions from any network finalize on Push Chain, giving everyone a single source of truth and enabling the same app to be accessible by users of all chains. -
Single Transaction and Universal Fee Abstraction
Users sign just one transaction, regardless of their source chain and pay gas in any token. No more maintaining or swapping countless tokens to use an app. -
Deploy Once, Use Everywhere
Developers write and deploy smart contracts once (EVM or otherwise) with zero extra code — one deployment covers all chains.
Push Chain is the first to bake these features directly into its consensus and runtime, truly eliminating fragmentation — no workarounds, no extra layers, just one universal chain for everyone.
Competitors
What sets Push Chain apart from other Universal Solutions?
Today's so-called "universal" solutions still rely on bridges, require double transactions or centralized relayers to move data and value. Push Chain is different—it's the first true universal L1 that:
-
Unifies users across chains
Every blockchain address is natively supported. Wallets like MetaMask, Phantom, etc are all compatible with Push Chain. Gas is paid in any token on any chain. -
Acts as a universal execution layer
All transactions finalize on the same chain, ensuring everyone interacts with the same app—no hacks, no workarounds. -
Correctly attributes & executes any chain's transactions
Transactions are signed, verified, and attributed to wallets on their source chains. A true universal chain supports them all.
How is this different from bridges or messaging layers?
Short Answer: Push is where your app runs. Bridges/messaging just move tokens or messages between chains which complicates everything for the user and developers.
-
Single home vs many clones
With bridges/messaging you deploy per chain and sync via messages. On Push you deploy once; everyone hits the same contract and shared state. -
No wrapped assets or mandatory bridging
Users stay on their home chain and pay with what they already hold; we handle routing and fee conversion under the hood. -
Unified identity & verification
We accept signatures from any wallet/chain and attribute them to the same user on Push — non-custodial. -
Fewer moving parts
No cross-chain approval dance, no gas-token hunting, no glue contracts to keep in sync. -
Bridges introduce complexity. Chain-native interop solves it
Bridges require complex engineering effort, time, audit cost and additional infrastructure. Chain-native interop just works as your app natively inherits it.
Result: simpler apps, one source of truth, and a UX that feels like one chain — even when users aren't.
How is Push Chain different from LayerZero?
LayerZero:
- Messaging Protocol: Enables cross-chain message passing
- Relayer Dependency: Relies on external relayers and oracles
- Developer Integration: Apps must integrate LayerZero SDK
- Trust Assumptions: Users must trust relayer infrastructure
Push Chain:
- Native Execution: Direct transaction execution from any chain
- No Relayers: Built-in cross-chain functionality at protocol level
- Zero Integration: Existing apps work without modifications
- Trust-Minimized: No extra trust assumptions beyond Push Chain’s own consensus
Push Chain provides native cross-chain execution while LayerZero requires additional infrastructure and integration.
How is Push Chain different from Wormhole?
Wormhole:
- Bridge Protocol: Primarily focused on token and NFT bridging
- Wrapped Assets: Creates wrapped versions of tokens on different chains
- Guardian Network: Relies on validator set to verify cross-chain messages
- Multi-Step Process: Users must bridge assets before using apps
Push Chain:
- Universal Execution: Users interact directly without bridging
- Native Assets: No wrapped tokens needed, use original assets
- Direct Verification: Native signature verification from any chain
- Single Transaction: Users interact in one step, no bridging required
Push Chain eliminates the need for asset bridging while Wormhole requires it for cross-chain interactions.
How is Push Chain different from Axelar?
Axelar:
- Network of Networks: Connects chains through Axelar network
- Validator Dependency: Relies on Axelar validator set for security
- Gateway Contracts: Requires gateway deployments on each chain
- Message Passing: Focuses on cross-chain communication
Push Chain:
- Direct Execution: Transactions process natively on Push Chain without intermediaries
- Independent Security: Own consensus without external dependencies
- Universal Contracts: Single deployment works for all chains
- Native Execution: Direct transaction processing from any chain
Push Chain provides direct universal access while Axelar adds an intermediate layer.
How is Push Chain different from Chainlink CCIP?
Chainlink CCIP:
- Oracle Network: Uses Chainlink oracle infrastructure
- Message Routing: Routes messages between different chains
- External Dependency: Relies on Chainlink's decentralized network
- Integration Required: Apps must integrate CCIP for cross-chain features
Push Chain:
- Built-in Protocol: Cross-chain functionality is native to the blockchain
- Direct Execution: No external oracle network needed
- Self-Contained: All verification and execution happens on Push Chain
- Automatic Compatibility: Deploy existing contracts — they work out of the box for all users
Push Chain has cross-chain capabilities built into its core protocol while CCIP is an external service layer.
How is Push Chain different from Particle Network?
Particle Network:
- Account Abstraction Focus: Primarily focuses on wallet abstraction and social login
- Multi-Chain Wallets: Creates unified wallet experience across chains
- SDK Integration: Requires integration of Particle SDK for functionality
- User Experience Layer: Operates as a layer on top of existing chains
Push Chain:
- Universal Blockchain: Native blockchain that supports all chain users
- Protocol-Level Integration: Cross-chain functionality built into consensus
- No SDK Required: Existing wallets work natively without modification
- Base Layer: Provides the underlying blockchain infrastructure, not just a UX layer
Push Chain is a universal blockchain while Particle Network is a wallet abstraction service.
How is Push Chain different from AggLayer?
AggLayer (Polygon):
- Aggregation Layer: Aggregates liquidity and state across Polygon chains
- Polygon Ecosystem: Specifically designed for Polygon CDK chains
- Shared Sequencing: Provides unified sequencing for connected chains
- Ecosystem Specific: Limited to Polygon's chain ecosystem
Push Chain:
- Universal Chain: Works with any blockchain, not ecosystem-specific
- Native Execution: Direct transaction execution from any chain
- Chain Agnostic: Supports Ethereum, Solana, Bitcoin, and all others
- One Deployment, Universal Apps: Deploy a smart contract once on Push Chain, and it becomes accessible to users from any chain — enabling true app-level interoperability
Push Chain enables universal applications with a single deployment across all blockchains, while AggLayer is focused on liquidity and sequencing aggregation within the Polygon ecosystem.
How is Push Chain different from Cosmos?
While both enable cross-chain functionality, the approaches are fundamentally different:
Cosmos:
- Hub-and-Spoke Model: Chains connect through IBC protocol
- Separate Ecosystems: Each chain maintains its own state and users
- Manual Bridging: Users must bridge assets between chains
- Developer Complexity: Need to deploy on multiple chains
Push Chain:
- Universal Chain: Single chain that natively supports all users
- Shared State: One unified state accessible from any chain
- No Bridging: Users interact directly from their origin chain
- Deploy Once: Single deployment works for all chain users
Push Chain removes the need for manual bridging and multi-chain deployments, offering a simpler, unified UX.
How is Push Chain different from Polkadot?
Polkadot:
- Parachain Model: Limited slots for connected chains
- Relay Chain Dependency: All parachains depend on relay chain security
- Substrate Framework: Requires specific development framework
- Auction System: Expensive parachain slot auctions
Push Chain:
- Universal Support: Natively supports any existing chain
- Independent Security: Own consensus and validator set
- EVM Compatible: Use existing Ethereum tools and contracts
- No Auctions: Direct integration without competitive bidding
Push Chain integrates with existing chains directly, while Polkadot requires chains to be rebuilt as parachains.
Token Related
Will there be a new token associated with Push Chain?
As a new layer 1, Push Chain would have its own native token with tokenomics suited to the functioning, maintenance, and security of a blockchain.
For full details, see our Tokenomics deep dive 👀.
Developers, Users and Node Operators
Are there incentives for early adopters or node operators on Push Chain?
Node operators will earn staking rewards once mainnet launches and are encouraged to take part in Push Points Program to earn rewards.
Early adopters are encouraged to take part in Push Points Program to earn rewards. Start by visiting Push Portal.
What benefits does Push Chain offer to developers and users?
🧙 For Developers
-
Deploy Once, 10× Your Reach
Deploy your App a single time — no code changes — and it runs on every supported chain, even non-EVM networks. -
Audit-Friendly, 100% EVM Compatible
Leverage existing Solidity contracts without extra audits or rewrites—focus your budget on features, not infrastructure. -
Unified, Frictionless UX
Users sign one transaction, pay in any token, and interact via any wallet — your app just works everywhere. -
Lightning-Fast DX
Spin up with our SDKs, virtual editors, and React playgrounds; go from zero to live in minutes.
🦹 For Users
-
One-Click Onboarding
Login with email, social, or any existing wallet — no more seed phrases or chain-hopping. -
Seamless Interactions
Gas, wallet, and chain complexities are hidden — enjoy apps as if they were native to your network. -
We're Fast
Transactions finalize in 1-2 seconds, feels like native to the chain you are on.
How can developers start building on Push Chain?
🚀 Visit our Documentation Hub to get everything you need:
- 🖥️ Virtual Code Editors: Spin up SDK function calls in your browser
- ⚛️ React Playground: Prototype your frontend in real time
- 📚 End-to-End Examples: Follow complete project walkthroughs
You'll have a sample app live in minutes—no local setup required!
DAO and Grants
How will the current governance system change when the new token launches?
The Push DAO governance system will both evolve and expand as Push Chain launches. This is an expected process, since Push is becoming something more encompassing than the original.
Delegates, ambassador programs, subDAOs, and other DAO initiatives will be upgraded to reflect the key goals of achieving status as the hub for universal applications, run by all of the groups that make them possible.
Doubts
What Happens to Push Notification and Push Chat?
Push Chain is a natural evolution of Push Protocol's vision. Current services of Push Protocol remain a priority, ensuring they continue to improve while benefiting from the new infrastructure.
Today's push notification and chat protocols will benefit significantly from being built on top of Push Chain. A dedicated section of the team will focus on maintaining and enhancing these protocols, ensuring they remain the de-facto standard in their respective domains.
By aligning with Push Chain, notifications and chat sent through the protocols will be processed as transactions on the chain. This integration not only enables these protocols to accrue value but also marks the beginning of a new chapter in their evolution, further enhancing their utility and impact within the web3 ecosystem.
Is this project a distraction from improving current services?
No, read ☝️ above.
Is Push Chain a shift away from Push Protocol's core focus on notifications and chat?
No. Push Chain builds upon Push Protocol's established foundation. Push Chain represents the next evolution of Push Protocol, not a departure.
How will the launch of Push Chain affect existing partnerships and integrations?
Push Chain complements existing partnerships by offering additional capabilities like cross-chain support, faster finality, and scalable solutions. It strengthens collaborations by enabling partners to build and scale universal applications.
How will Push Chain maintain decentralization while scaling?
Our Devnet demonstrated how we'll scale using dynamic sharding and parallel execution—boosting throughput without compromising decentralization.
On testnet, we focused on full stack interop with the chain running on CometBFT, a battle-tested, Byzantine-fault-tolerant engine. The network achieved sub-second finality and has the ability to handle up to 20k transactions per minute.
This proof of concept is just the beginning. As we roll out further scaling optimizations in later phases, we're confident Push Chain can meet the demands of universal applications—securely and without centralization.
Are there any risks of centralization with Push Chain?
No. Push Chain's architecture emphasizes decentralization.
Push Chain is fully decentralized and is designed to be robust and resilient. Anyone can run a node and participate in the network and is incentivized or penalized through PoS. To Summarize:
- Validators and other actors operate independently and are incentivized through PoS.
- Governance mechanisms ensure community involvement.
- Every ecosystem party is included in governance to some extent.
To learn more about how to run a node, see our Knowledge Base or check out our Validator Node Repo.
Support and Engagement
I need help, where can I contact Push Chain?
For support, you can submit a ticket over here or reach out to us on support@push.org.
If you are a developer, you can also reach out to us on our Discord and we will be happy to help you.
Great, how can I contribute?
The best way to stay on top of Push Chain's progress is through the official Push channels: website, Twitter/X, Telegram, and Discord.
Always stay cautious of phishing attempts, fake sites, or scams asking for your crypto. All official communications will go out from our official Push handles.